How Occupational Therapy (OT) Addresses Fine Motor Skills and Printing
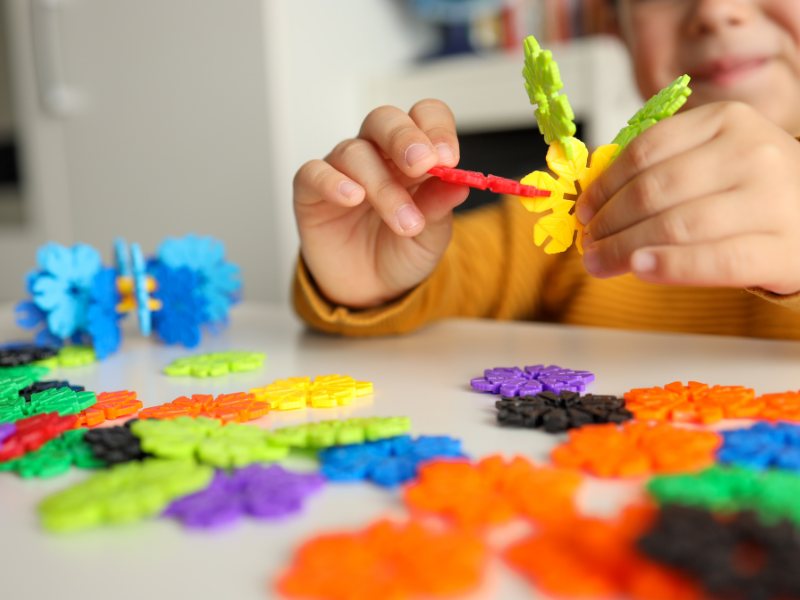
Occupational Therapy (OT) helps children develop fine motor skills and improve printing abilities. Fine motor skills involve the coordination of small muscles, particularly in the hands and fingers, to perform precise movements.
Through targeted interventions and individualized support, occupational therapy plays a vital role in helping individuals develop the fine motor skills and printing abilities necessary for successful participation in daily life and educational activities.
Assessment
- Occupational therapists begin with a comprehensive assessment to identify specific fine motor deficits and challenges in printing. This includes evaluating grip strength, hand dexterity, coordination, and handwriting samples.
Therapeutic Intervention
Strengthening and Dexterity Exercises:
- Therapists use a variety of activities to improve hand strength and finger dexterity. These can include play-based tasks.
Handwriting Skills Development:
- OT interventions focus on the fundamental skills necessary for handwriting. This includes teaching proper pencil grip, posture, and paper positioning. Using structured programs and tools, Occupational Therapists address legibility and printing speed.
Fine Motor Coordination Activities:
- Activities designed to enhance hand-eye coordination and bilateral coordination (using both hands together) are integral. Examples include cutting with scissors, drawing, colouring within lines, and completing puzzles.
Adaptive Tools and Techniques:
- For individuals with significant difficulties, adaptive tools such as special grips, slant boards, or weighted pencils to make writing easier may be recommended.
- Techniques such as breaking down tasks into smaller steps, providing visual aids, and using tactile feedback are also employed to support learning.
Environmental and Task Modifications:
- Modifying the environment and tasks to reduce barriers to fine motor skill development is another approach. This might involve adjusting the height of the desk, using larger lined paper, or providing a stable surface for writing – for creating functional activities.
Practice and Repetition:
- Consistent practice and repetition of fine motor tasks and printing exercises are crucial. Therapists often create engaging and varied practice opportunities to keep individuals motivated.
Collaboration and Education:
- OT involves collaboration with parents, teachers, and caregivers to ensure consistent support and practice outside of therapy sessions. Education on reinforcing skills at home and in the classroom is provided.
Impact of OT on Fine Motor Skills and Printing:
- Improved Hand Function: Strengthening and coordination exercises lead to better hand function and precision in tasks requiring fine motor skills.
- Enhanced Writing Skills: Structured handwriting programs and practice improve legibility, speed, and confidence in writing.
- Increased Independence: Mastery of fine motor skills contributes to greater independence in daily activities such as dressing, feeding, and school-related tasks.
- Positive Academic and Social Outcomes: Improved printing and fine motor abilities can lead to better academic performance and more positive social interactions, as the individual can more effectively participate in classroom activities, self-care tasks and play.
SUPPORTS AT EPA for KIDS
- Individual supports (1:1 sessions)
- Group treatment options – ie: Writing Warriors Cam